Evaluation suggests {that a} possible widespread ancestor of the Indo-European languages, comprising English and Sanskrit, might have been spoken round 8,100 years in the past.

Scientists, together with these from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Germany, have declared that their analysis is a “important breakthrough” in comprehending the beginnings of Indo-European languages, a debate that endured for nearly 2 hundred years.
Two theories have been proposed in an effort to clarify the origins of the household of languages presently utilized by near half of the world’s inhabitants.
The Steppe speculation means that the beginnings of this may be traced again to the Pontic-Caspian Steppe area roughly 6,000 years in the past.
The “Anatolian” or “farming” speculation proposes that the origin of one thing is related to the graduation of agriculture about 9,000 years in the past.
Nonetheless, prior analysis regarding the Indo-European language household has drawn differing outcomes as a consequence of sure inaccuracies and inconsistencies throughout the information utilized.
With a view to handle these deficits, a collective of 80+ language specialists from around the globe compiled a corpus of core phrases from 161 Indo-European languages, which embody 52 historic or historic languages.
A latest evaluation, showing in Science, investigated whether or not outdated written dialects, resembling Classical Latin and Vedic Sanskrit, had been the rapid forerunners of recent Romance and Indic tongues, respectively.
Researchers performed an examination of the shared origins of the core lexicon in 100 present languages and 51 archaic languages.
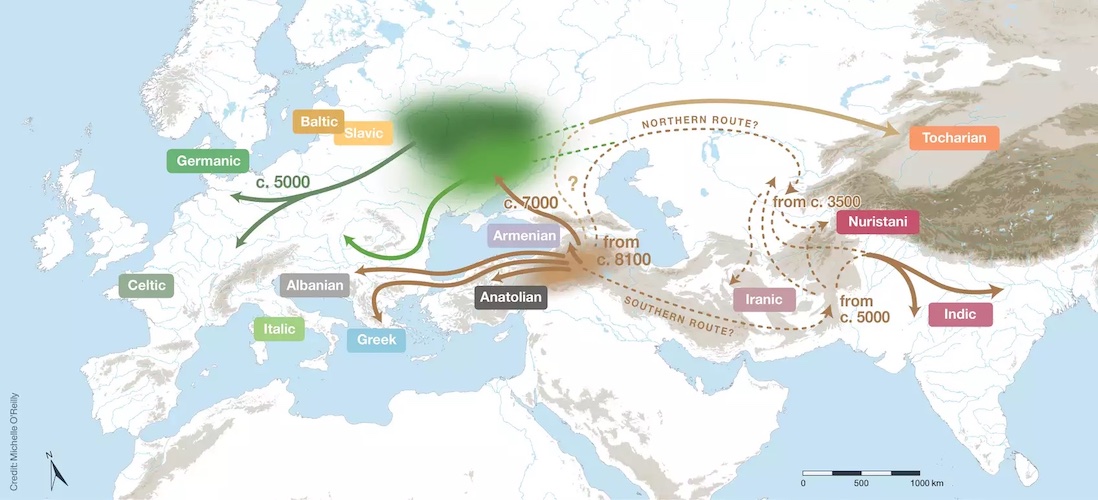

It seems, based on the analysis, that the Indo-European language household has been in existence for 8,100 years and that by 7,000 years in the past, 5 main branches had already been divided from it.
In keeping with co-author Russell Grey, the chronology of the examine stays sturdy when examined towards varied phylogenetic fashions and sensitivity analyses.
Dr Grey asserted {that a} mixture of historic DNA and language phylogenetics might present the reply to the long-standing Indo-European enigma, which is a mixture of the farming and Steppe hypotheses.
Based mostly on the most recent investigations, a hybrid speculation has been advised for the inception of the Indo-European languages. It proposes a main homeland south of the Caucasus and a secondary residence on the Steppe, by means of which a few of the Indo-European languages arrived in Europe with the migrations of the Yamnaya and Corded Ware individuals.
Paul Heggarty, a contributor to the examine, said that the latest historic DNA information factors to the Anatolian department of Indo-European originating from someplace close to the northern arc of the Fertile Crescent, moderately than from the Steppe.
Dr. Heggarty advised that the language household tree topology and lineage cut up dates level to different branches that doubtless unfold from that space straight, not by means of the Steppe.



